網站首頁 編程語言 正文
給定一組樣本,{1,5},{2,7},{3,9},{4,11},{5,13},根據樣本預測一元線性方程y=wx+b中的w值和b值,可以用數學的最小二乘法求解,這里使用批量梯度下降法求解。
主要思想:根據y=wx+b計算出來的y值和實際y值是有誤差的,根據這個誤差去更新w和b的值(具體計算公式需要用到偏導數,程序中的變量“xxSum”體現了“批量”),更新速度快慢取決于學習率的大小,當w和b的值幾乎不再更新時,意味計算出來的y值和實際y值的誤差已經很小,這時候停止迭代,求解完成。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void LinearRegression(float x[], float y[], int n, float& w, float& b)
{
float yOut;
float residual;
float deltaB = 0.0;
float deltaBSum = 0.0;
float deltaW = 0.0;
float deltaWSum = 0.0;
float learningRate = 0.01;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
yOut = w * x[i] + b;
residual = -(yOut - y[i]);
deltaB = 1 * residual * learningRate;
deltaBSum = deltaBSum + deltaB;
deltaW = x[i] * residual * learningRate;
deltaWSum = deltaWSum + deltaW;
}
deltaB = deltaBSum / n;
deltaW = deltaWSum / n;
b = b + deltaB;
w = w + deltaW;
}
int main()
{
clock_t t1 = clock();
float x[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; //樣本x值
float y[] = { 5, 7, 9, 11, 13 }; //樣本y值
int n = 5;
float w = 1.0; //隨機初始權重
float b = 1.0; //隨機初始偏移
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
float preW = w;
float preB = b;
LinearRegression(x, y, n, w, b);
if (fabs(w - preW) < 0.000001 && fabs(b - preB) < 0.000001)
break;
}
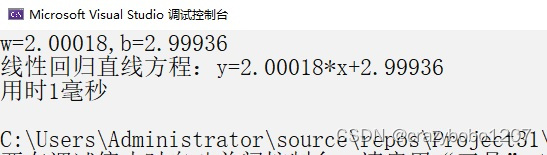
cout << "w=" << w << "," << "b=" << b << endl;
cout << "線性回歸直線方程:y=" << w << "*x+" << b << endl;
clock_t t2 = clock();
cout << "用時" << t2 - t1 << "毫秒" << endl;
return 0;
}運行結果如下:
下面驗證以上線性回歸的結果是否正確(其實可以直接觀察到y=2*x+3就是準確解,以上求得的w和b值,與真實值之間的誤差是萬分之幾)。
#include <GL/glut.h>
#include <math.h>
const float ratio = 15.0;
const int pointNum = 5;
const float w = 2.00018;
const float b = 2.99936;
struct Point
{
float x;
float y;
};
Point p[pointNum] = { {1,5},{2,7},{3,9},{4,11},{5,13} };
void draw()
{
glPointSize(1);
glColor3f(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glVertex2f(-1.0, 0);
glVertex2f(1.0, 0);
glEnd();
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glVertex2f(0, -1);
glVertex2f(0, 1.0);
glEnd();
glPointSize(5);
glColor3f(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
for (int i = 0; i < pointNum; i++)
{
glVertex2f(p[i].x / ratio, p[i].y / ratio);
}
glEnd();
glPointSize(3);
glColor3f(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glVertex2f(0.0 / ratio, (w * 0.0 + b) / ratio);
glVertex2f(10.0 / ratio, (w * 10.0 + b) / ratio);
glEnd();
glFlush();
}
void myDisplay()
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
draw();
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB | GLUT_DEPTH);
glutInitWindowPosition(100, 100);
glutInitWindowSize(600, 600);
glutCreateWindow("Draw");
glutDisplayFunc(myDisplay);
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
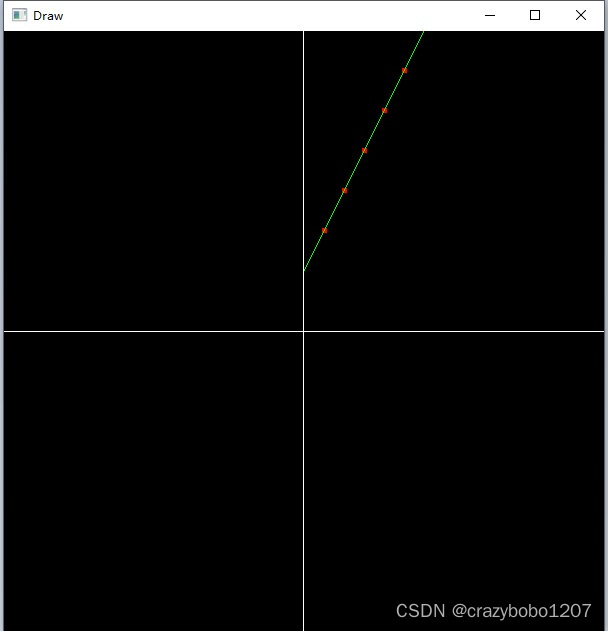
}畫出5個樣本點,以及y=2.00018*x+2.99936的直線方程,直線基本穿過5個樣本點。
原文鏈接:https://blog.csdn.net/crazybobo1207/article/details/133592331
- 上一篇:沒有了
- 下一篇:沒有了
相關推薦
- 2022-12-06 詳解從ObjectPool到CAS指令_C#教程
- 2022-05-21 C語言實現銷售管理系統課程設計_C 語言
- 2022-08-18 KubeSphere分級管理實踐及解析_云其它
- 2022-10-20 Android?PowerManagerService?打開省電模式_Android
- 2023-02-12 React實現錨點跳轉組件附帶吸頂效果的示例代碼_React
- 2022-08-22 C++貪心算法處理多機調度問題詳解_C 語言
- 2022-06-02 C#?操作Windows注冊表的實現方法_C#教程
- 2022-12-07 C++?Boost?Container庫示例詳細講解_C 語言
- 欄目分類
-
- 最近更新
-
- window11 系統安裝 yarn
- 超詳細win安裝深度學習環境2025年最新版(
- Linux 中運行的top命令 怎么退出?
- MySQL 中decimal 的用法? 存儲小
- get 、set 、toString 方法的使
- @Resource和 @Autowired注解
- Java基礎操作-- 運算符,流程控制 Flo
- 1. Int 和Integer 的區別,Jav
- spring @retryable不生效的一種
- Spring Security之認證信息的處理
- Spring Security之認證過濾器
- Spring Security概述快速入門
- Spring Security之配置體系
- 【SpringBoot】SpringCache
- Spring Security之基于方法配置權
- redisson分布式鎖中waittime的設
- maven:解決release錯誤:Artif
- restTemplate使用總結
- Spring Security之安全異常處理
- MybatisPlus優雅實現加密?
- Spring ioc容器與Bean的生命周期。
- 【探索SpringCloud】服務發現-Nac
- Spring Security之基于HttpR
- Redis 底層數據結構-簡單動態字符串(SD
- arthas操作spring被代理目標對象命令
- Spring中的單例模式應用詳解
- 聊聊消息隊列,發送消息的4種方式
- bootspring第三方資源配置管理
- GIT同步修改后的遠程分支
